Key Functions of Retail Banking VS Corporate Banking

Retail Banking and Corporate Banking; two established dominant verticals in the financial ecosystem cater to business-to-consumer (B2C) and business-to-business (B2B) segments of society. The retail business is a model built for the general public while the corporate banking model aims at MSMEs and large-sized businesses.
Key Differences
| Key Basis | Retail Banking | Corporate Banking |
| Nature of Products and Services | Standardized | Tailor-made |
| Customer/Client Base | Large | Small |
| Processing Cost | Low | High |
| Value of Transactions | Low value of transactions | High value of transactions |
| Profitable | Low | High |
| Customer Relationship | On low priority | On high priority |
Retail Banking
The main goal of financial institutions is to provide the population with financial assistance, whether credit or wealth management. The combined net profit of all the retail banks in India amounts to Rs. 224,054 crores as of May 2021.
With Citi Bank looking to exit the retail market in India owing to its strategic review, large conglomerates like Axis Bank are bidding for the said fragment owing to its high clientele base and prospects.
Key Functions
Retail banks offer a variety of products and services to the general public. Fundamental services include prototypical savings accounts, types of mortgages, loans, etc at high-interest rates. It also includes services like plastic cards and remittance services which prove to be profitable offerings for retail banks.
The financial personality of an individual helps in deciding the service and the extent to which an offering can be availed. For instance, High Networth Individuals (HNI) receive tailor-made services along with a personal relationship manager owing to the business they give to a bank.
Corporate Banking
Corporate banking is a subset of business banking that involves a range of banking services that are offered only to corporates. The clientele base associated with business banking is limited yet regarded as a high priority owing to the magnitude of transactional business with the banks.
Key Functions
Corporate banks earn profits by sanctioning credit. Their area of operation also includes managing the cash flow of the corporate, treasury handling, currency conversion, etc.
Depending upon expansion plans and needs, corporate banks devise tailor-made credit options for corporations they cater to. For instance, equipment loans, manufacturing loans, etc. They also indulge in trade finance, bill collection, credit letters, payroll management and much more for the corporations they represent.
With intense competition taking over the market, corporate banks also offer real estate analysis, portfolio evaluation, debt and equity structuring, asset management and so on.
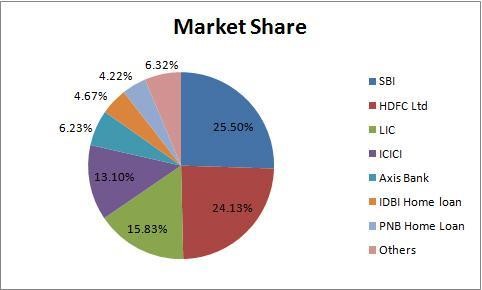
Source: https://seekingalpha.com/article/3604876-indian-banks-set-to-boom-consider-buying-state-bank-of-india
Conclusion
Most large banks have a separate division for the retail and corporate functions as both guarantee great profit.
The existence of both wings of banking is essential for the healthy functioning of local and global economies. While one brings in deposits from personal customers (Retail Banking), which in turn enables corporate banking to offer expansion assistance to companies, further leading to the creation of jobs that aid in the expansion of economies.

