The Growth of MSMEs in India
Micro, small and medium enterprises are playing a vital role in the growth of the Indian economy. They contribute to roughly 30% of India’s GDP while employing a whopping 11.10 crore Indians in various sectors of functionality. Given the fact that the majority, i.e., 65% of the Indian population is below the age of 35, job generation is a very significant part of overall economic growth. Amidst this, the question arises, how are MSMEs treated in India and what is their growth prospect?
With the launch and shift towards technology-driven services, MSMEs are regarded as the new worthwhile and remunerative sector by several tech-driven companies. They are not just targeting MSMEs at a broader level but launching customized services targeted specifically at the 63 million MSMEs. These services not only give tech-driven companies a larger audience to serve but also ensure MSMEs expand and contribute toward sustainable growth.
Growth chart of Indian MSMEs
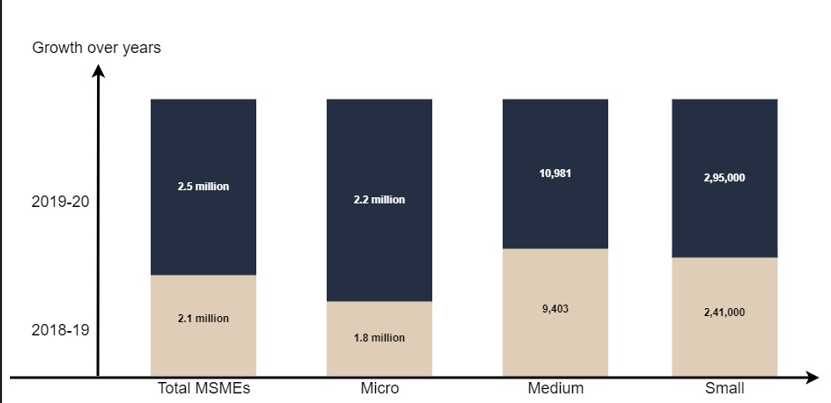
Source: https://www.livemint.com/opinion/online-views/india-needs-an-ecosystem-that-s-conducive-to-msme-expansion-11629736194548.html
As per reports and shown in the chart, the percentage of registered MSMEs across sizes grew by 18.5% YoY. Furthermore, the number of registered MSMEs increased from 2.1 million to 2.5 million between 2018-2020. Micro, small and medium-sized enterprises have all shown positive growth during the mentioned span.
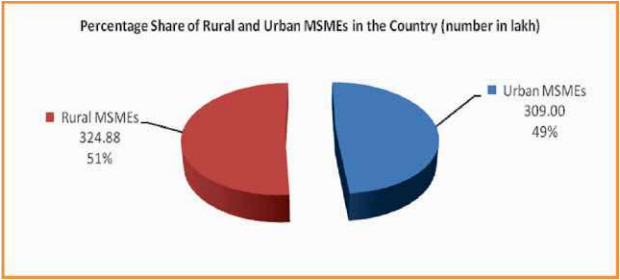
Source: RBI Report
As per the chart, the percentage share of Urban and Rural MSMEs is almost at par with 49% and 51% respectively. While Urban MSMEs have higher access to financial services, rural MSMEs are more in need of assistance in every aspect of growth.
The idea is to nurture and grow the opportunities we present to these and new MSMEs irrespective of their geographical location or the product they sell. This will allow us to launch and handhold initiatives that will ensure these MSMEs are more exposed to opportunities and financial services.
A major known stake is owned by trading followed by manufacturing at 230.35 lakh and 196.5 lakh respectively. Keeping this in mind, efforts must be made to focus on aided trading and quality manufacturing to benefit the end users as well. Leveraging automation to enhance operations, use of technology for data analytics, venturing into new markets through e-commerce, providing them subsidies, equipping them with education and so on, MSMEs can be given the assistance they have missed for so long. The regulators can further chalk out formal plans and frameworks to standardize the functions of MSMEs thereby instilling a sense of inclusiveness in MSMEs to strive harder at what they are already doing; building the nation.
While building the said framework, regulators can ensure that these policies are inclined towards boosting small production units, compliance is easy on MSMEs and their growth plan is well defined to enable MSMEs to introduce themselves to global markets thereby ensuring financial inclusion for themselves.

